I am a PhD student (2021-) at the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems where I am advised by MPI Director Michael Black. Earlier, I worked as an Applied Scientist at Amazon (2019-2021). I earned my Masters (2017-2019) from the Robotics Institute, Carnegie Mellon University, working with Prof. Kris Kitani. I am a recipient of the Meta Research PhD Fellowship award in 2023.
At Amazon Lab126, I closely collaborated with Prof. James Rehg, Dr. Amit Agrawal and Dr. Ambrish Tyagi. In 2023, I spent time at Epic Games as a research intern working with Dr. Carsten Stoll, Dr. Christoph Lassner and Dr. Daniel Holden. Recently, I interned at Meta Zurich where I worked with Dr. Bugra Tekin on impoving spatial understanding and visual grounding in 3D foundation models (VLMs).
It has been my great fortune to have worked with excellent mentors and advisors.
Work Experience




Recent News
- Oct 2025: 🎉 1 paper accepted in ICCV 2025 - SDFit
- Jun 2025: 🏆 Selected for the Doctoral Consortium at CVPR 2025
- Jun 2025: 🏆 InteractVLM won the Human Contact Estimation Challenge at CVPR 2025
- Jun 2025: 🏆 Received the Outstanding Reviewer Award for CVPR 2025
- Jun 2025: 🎉 2 papers accepted in CVPR 2025 - PICO, InteractVLM
- Jun 2025: 🎤 Organized two workshops at CVPR 2025: 3D HUMANS, RHOBIN
- Oct 2024: 💼 Started internship at Meta Zurich
Research
My research lies at the intersection of machine learning, computer vision and computer graphics. Specifically, I am interested in 3D modeling of human bodies, modeling human-object interactions, physics-inspired human motion understanding and spatial understanding of 3D scenes. In the past, I have worked on synthetic data for applications like object detection and human pose estimation from limited supervision.
Publications
InteractVLM: 3D Interaction Reasoning from 2D Foundational Models

PICO: Reconstructing 3D People In Contact with Objects
Workshop on Generating Digital Twins from Images and Videos (gDT-IV @ ICCV) 2025 - Oral
Workshop on Human-Robot-Scene Interaction and Collaboration (HRSIC @ ICCV) 2025 - Oral
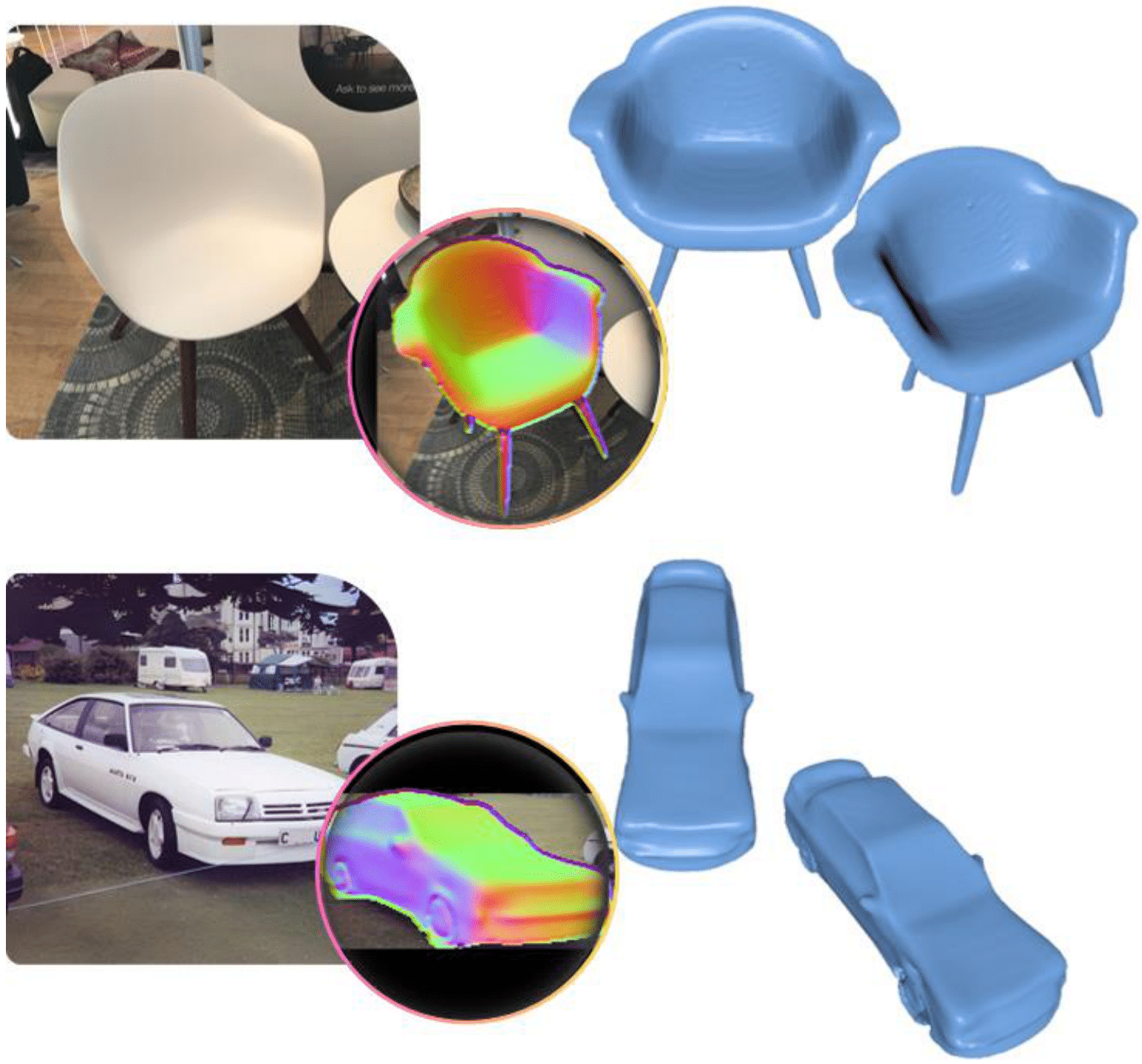
Recovering 3D Human-Object Interaction (HOI) from single color images is challenging due to depth ambiguities, occlusions, and the huge variation in object shape and appearance. Thus, past work requires controlled settings such as known object shapes and contacts, and tackles only limited object classes. Instead, we need methods that generalize to natural images and novel object classes. We tackle this in two main ways: (1) We collect PICO-db, a new dataset of natural images uniquely paired with dense 3D contact on both body and object meshes. To this end, we use images from the recent DAMON dataset that are paired with contacts, but these contacts are only annotated on a canonical 3D body. In contrast, we seek contact labels on both the body and the object. To infer these given an image, we retrieve an appropriate 3D object mesh from a database by leveraging vision foundation models. Then, we project DAMON's body contact patches onto the object via a novel method needing only 2 clicks per patch. This minimal human input establishes rich contact correspondences between bodies and objects. (2) We exploit our new dataset of contact correspondences in a novel render-and-compare fitting method, called PICO-fit, to recover 3D body and object meshes in interaction. PICO-fit infers contact for the SMPL-X body, retrieves a likely 3D object mesh and contact from PICO-db for that object, and uses the contact to iteratively fit the 3D body and object meshes to image evidence via optimization. Uniquely, PICO-fit works well for many object categories that no existing method can tackle. This is crucial to enable HOI understanding to scale in the wild. Our data and code are available.

HUMOS: HUman MOtion Model Conditioned on Body Shape
Generating realistic human motion is an important task in many computer vision and graphics applications. The rich diversity of human body shapes and sizes significantly influences how people move. However, existing motion models typically ignore these differences and use a normalized, average body size. This leads to a homogenization of motion across human bodies that limits diversity and that may not align with their physical attributes. We propose a novel approach to learn a generative motion model conditioned on body shape. We demonstrate that it is possible to learn such a model from unpaired training data using cycle consistency and intuitive physics and stability constraints that model the correlation between identity and movement. The resulting model produces diverse, physically plausible, dynamically stable human motions that are quantitatively and qualitatively more realistic than the existing state of the art.
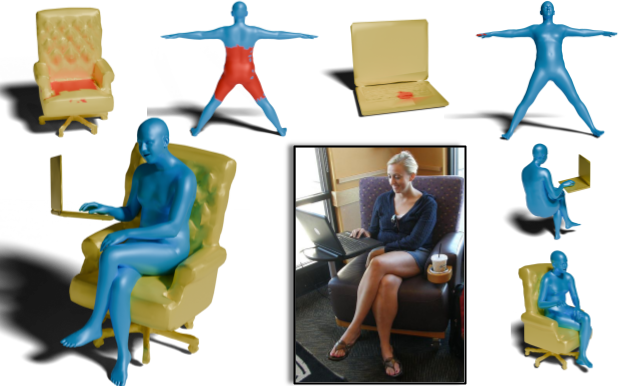
DECO: Dense Estimation of 3D Human-Scene COntact in the Wild
Understanding how humans use physical contact to interact with the world is key to enabling human-centric artificial intelligence. While inferring 3D contact is crucial for modeling realistic and physically-plausible human-object interactions, existing methods either focus on 2D, consider body joints rather than the surface, use coarse 3D body regions, or do not generalize to in-the-wild images. In contrast, we focus on inferring dense, 3D contact between the full body surface and objects in arbitrary images. To achieve this, we first collect DAMON, a new dataset containing dense vertex-level contact annotations paired with RGB images containing complex human-object and human-scene contact. Second, we train DECO, a novel 3D contact detector that uses both body-part-driven and scene-context-driven attention to estimate vertex-level contact on the SMPL body. DECO builds on the insight that human observers recognize contact by reasoning about the contacting body parts, their proximity to scene objects, and the surrounding scene context. We perform extensive evaluations of our detector on DAMON as well as on the RICH and BEHAVE datasets. We significantly outperform existing SOTA methods across all benchmarks. We also show qualitatively that DECO generalizes well to diverse and challenging real-world human interactions in natural images. The code, data, and models are available for research purposes.
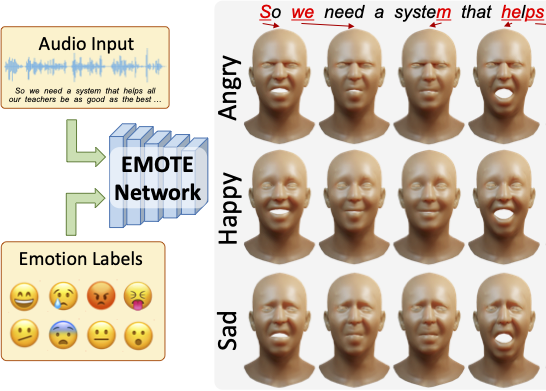
EMOTE: Emotional Speech-Driven Animation with Content-Emotion Disentanglement
To be widely adopted, 3D facial avatars must be animated easily, realistically, and directly from speech signals. While the best recent methods generate 3D animations that are synchronized with the input audio, they largely ignore the impact of emotions on facial expressions. Realistic facial animation requires lip-sync together with the natural expression of emotion. To that end, we propose EMOTE (Expressive Model Optimized for Talking with Emotion), which generates 3D talking-head avatars that maintain lip-sync from speech while enabling explicit control over the expression of emotion. To achieve this, we supervise EMOTE with decoupled losses for speech (i.e., lip-sync) and emotion. These losses are based on two key observations: (1) deformations of the face due to speech are spatially localized around the mouth and have high temporal frequency, whereas (2) facial expressions may deform the whole face and occur over longer intervals. Thus, we train EMOTE with a per-frame lip-reading loss to preserve the speech-dependent content, while supervising emotion at the sequence level. Furthermore, we employ a content-emotion exchange mechanism in order to supervise different emotions on the same audio, while maintaining the lip motion synchronized with the speech. To employ deep perceptual losses without getting undesirable artifacts, we devise a motion prior in the form of a temporal VAE. Due to the absence of high-quality aligned emotional 3D face datasets with speech, EMOTE is trained with 3D pseudo-ground-truth extracted from an emotional video dataset (i.e., MEAD). Extensive qualitative and perceptual evaluations demonstrate that EMOTE produces speech-driven facial animations with better lip-sync than state-of-the-art methods trained on the same data, while offering additional, high-quality emotional control.
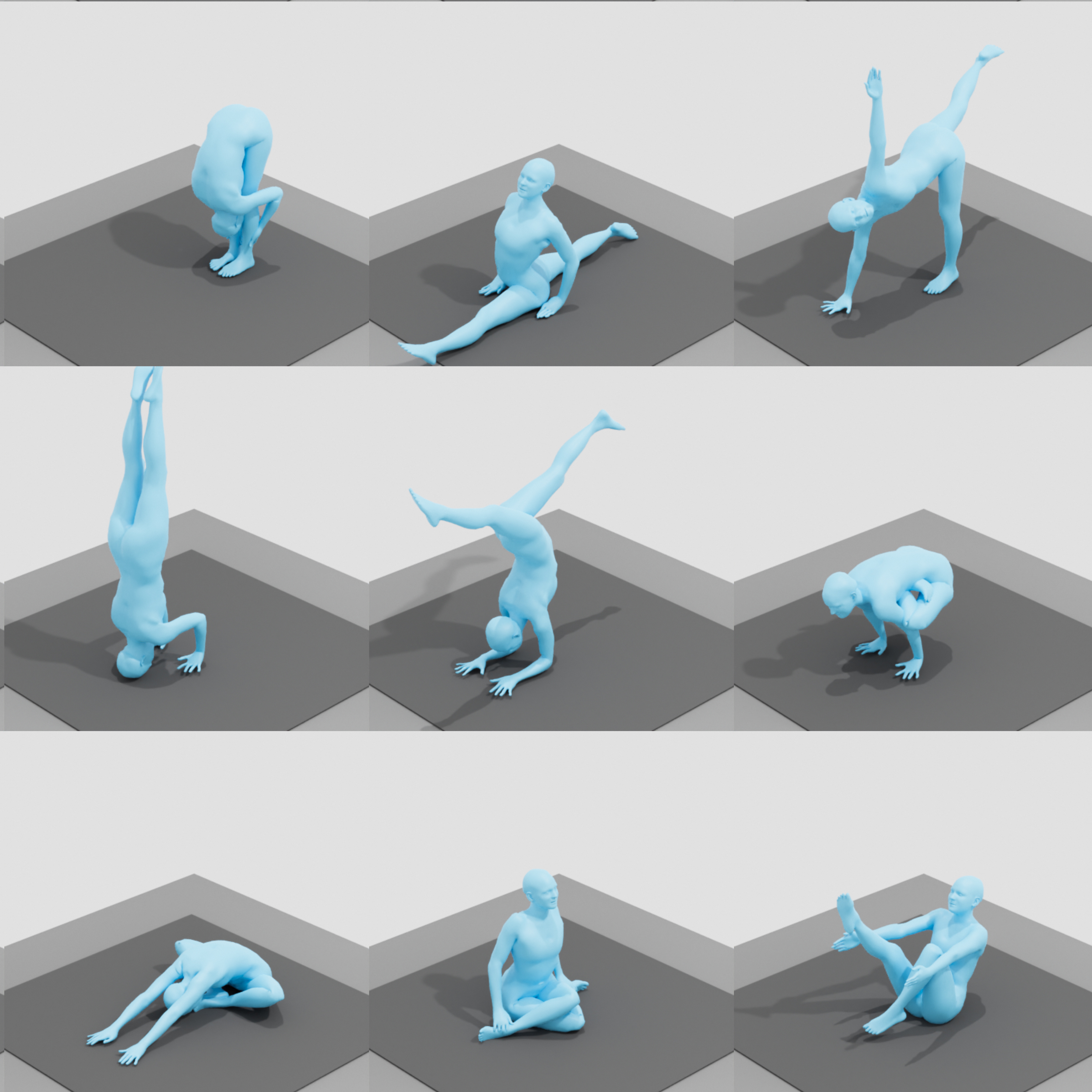
3D Human Pose Estimation via Intuitive Physics
The estimation of 3D human body shape and pose from images has advanced rapidly. While the results are often well aligned with image features in the camera view, the 3D pose is often physically implausible; bodies lean, float, or penetrate the floor. This is because most methods ignore the fact that bodies are typically supported by the scene. To address this, some methods exploit physics engines to enforce physical plausibility. Such methods, however, are not differentiable, rely on unrealistic proxy bodies, and are difficult to integrate into existing optimization and learning frameworks. To account for this, we take a different approach that exploits novel intuitive-physics (IP) terms that can be inferred from a 3D SMPL body interacting with the scene. Specifically, we infer biomechanically relevant features such as the pressure heatmap of the body on the floor, the Center of Pressure (CoP) from the heatmap, and the SMPL body's Center of Mass (CoM) projected on the floor. With these, we develop IPMAN, to estimate a 3D body from a color image in a "stable" configuration by encouraging plausible floor contact and overlapping CoP and CoM. Our IP terms are intuitive, easy to implement, fast to compute, and can be integrated into any SMPL-based optimization or regression method; we show examples of both. To evaluate our method, we present MoYo, a dataset with synchronized multi-view color images and 3D bodies with complex poses, body-floor contact, and ground-truth CoM and pressure. Evaluation on MoYo, RICH and Human3.6M show that our IP terms produce more plausible results than the state of the art; they improve accuracy for static poses, while not hurting dynamic ones. Code and data will be available for research.

BITE: Beyond Priors for Improved Three-Dog Pose Estimation
We address the problem of inferring the 3D shape and pose of dogs from images. Given the lack of 3D training data, this problem is challenging, and the best methods lag behind those designed to estimate human shape and pose. To make progress, we attack the problem from multiple sides at once. First, we need a good 3D shape prior, like those available for humans. To that end, we learn a dog-specific 3D parametric model, called D-SMAL. Second, existing methods focus on dogs in standing poses because when they sit or lie down, their legs are self occluded and their bodies deform. Without access to a good pose prior or 3D data, we need an alternative approach. To that end, we exploit contact with the ground as a form of side information. We consider an existing large dataset of dog images and label any 3D contact of the dog with the ground. We exploit body-ground contact in estimating dog pose and find that it significantly improves results. Third, we develop a novel neural network architecture to infer and exploit this contact information. Fourth, to make progress, we have to be able to measure it. Current evaluation metrics are based on 2D features like keypoints and silhouettes, which do not directly correlate with 3D errors. To address this, we create a synthetic dataset containing rendered images of scanned 3D dogs. With these advances, our method recovers significantly better dog shape and pose than the state of the art, and we evaluate this improvement in 3D. Our code, model and test dataset are publicly available for research purposes at https://bite.is.tue.mpg.de.
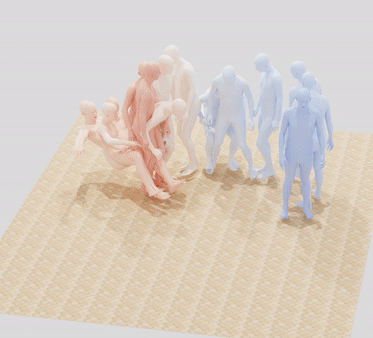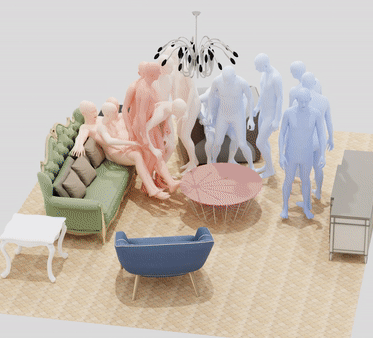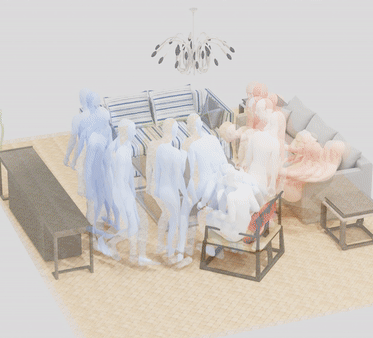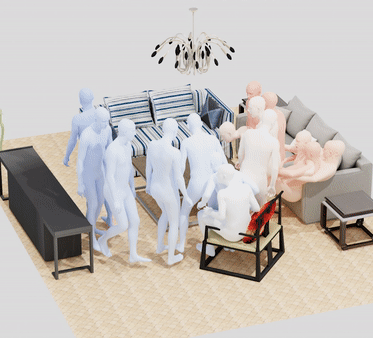
MIME: Human-Aware 3D Scene Generation
Generating realistic 3D worlds occupied by moving humans has many applications in games, architecture, and synthetic data creation. But generating such scenes is expensive and labor intensive. Recent work generates human poses and motions given a 3D scene. Here, we take the opposite approach and generate 3D indoor scenes given 3D human motion. Such motions can come from archival motion capture or from IMU sensors worn on the body, effectively turning human movement in a "scanner" of the 3D world. Intuitively, human movement indicates the free-space in a room and human contact indicates surfaces or objects that support activities such as sitting, lying or touching. We propose MIME (Mining Interaction and Movement to infer 3D Environments), which is a generative model of indoor scenes that produces furniture layouts that are consistent with the human movement. MIME uses an auto-regressive transformer architecture that takes the already generated objects in the scene as well as the human motion as input, and outputs the next plausible object. To train MIME, we build a dataset by populating the 3D FRONT scene dataset with 3D humans. Our experiments show that MIME produces more diverse and plausible 3D scenes than a recent generative scene method that does not know about human movement. Code and data will be available for research.
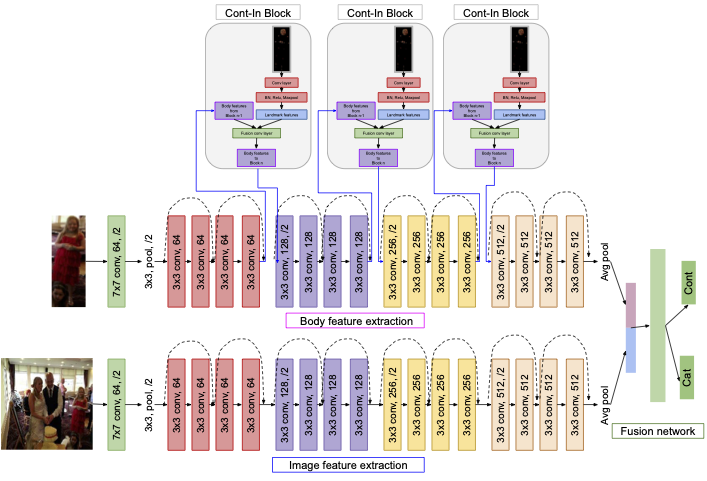
PERI: Part Aware Emotion Recognition in the Wild
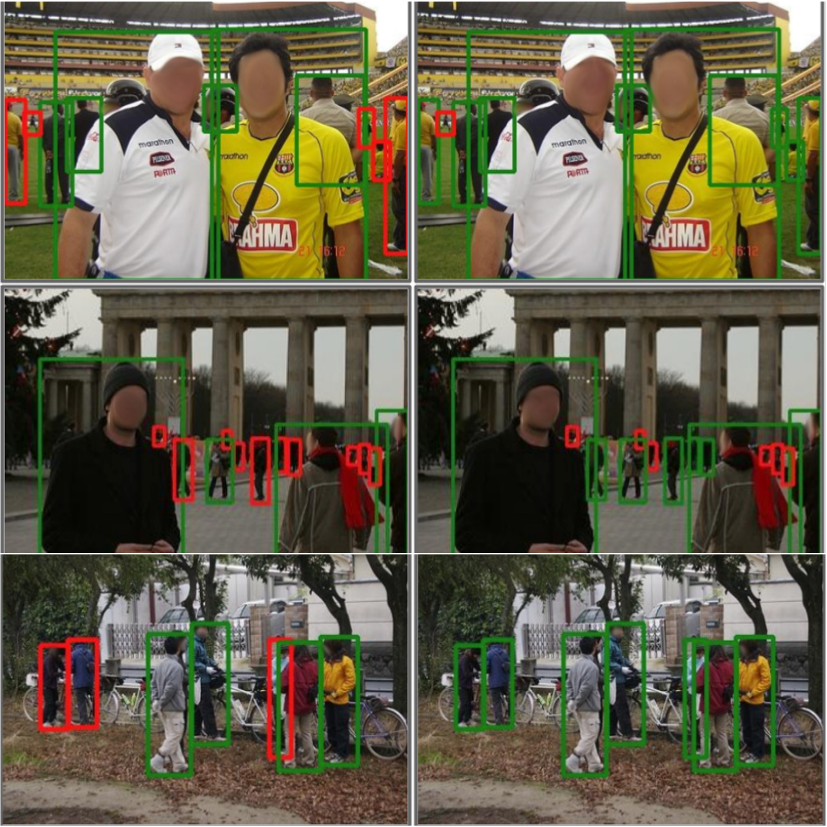
Top-down methods for monocular human mesh recovery have two stages: (1) detect human bounding boxes; (2) treat each bounding box as an independent single-human mesh recovery task. Unfortunately, the single-human assumption does not hold in images with multi-human occlusion and crowding. Consequently, top-down methods have difficulties in recovering accurate 3D human meshes under severe person-person occlusion. To address this, we present Occluded Human Mesh Recovery (OCHMR) - a novel top-down mesh recovery approach that incorporates image spatial context to overcome the limitations of the single-human assumption. The approach is conceptually simple and can be applied to any existing top-down architecture. Along with the input image, we condition the top-down model on spatial context from the image in the form of body-center heatmaps. To reason from the predicted body centermaps, we introduce Contextual Normalization (CoNorm) blocks to adaptively modulate intermediate features of the top-down model. The contextual conditioning helps our model disambiguate between two severely overlapping human bounding-boxes, making it robust to multi-person occlusion. Compared with state-of-the-art methods, OCHMR achieves superior performance on challenging multi-person benchmarks like 3DPW, CrowdPose and OCHuman. Specifically, our proposed contextual reasoning architecture applied to the SPIN model with ResNet-50 backbone results in 75.2 PMPJPE on 3DPW-PC, 23.6 AP on CrowdPose and 37.7 AP on OCHuman datasets, a significant improvement of 6.9 mm, 6.4 AP and 20.8 AP respectively over the baseline. Code and models will be released.
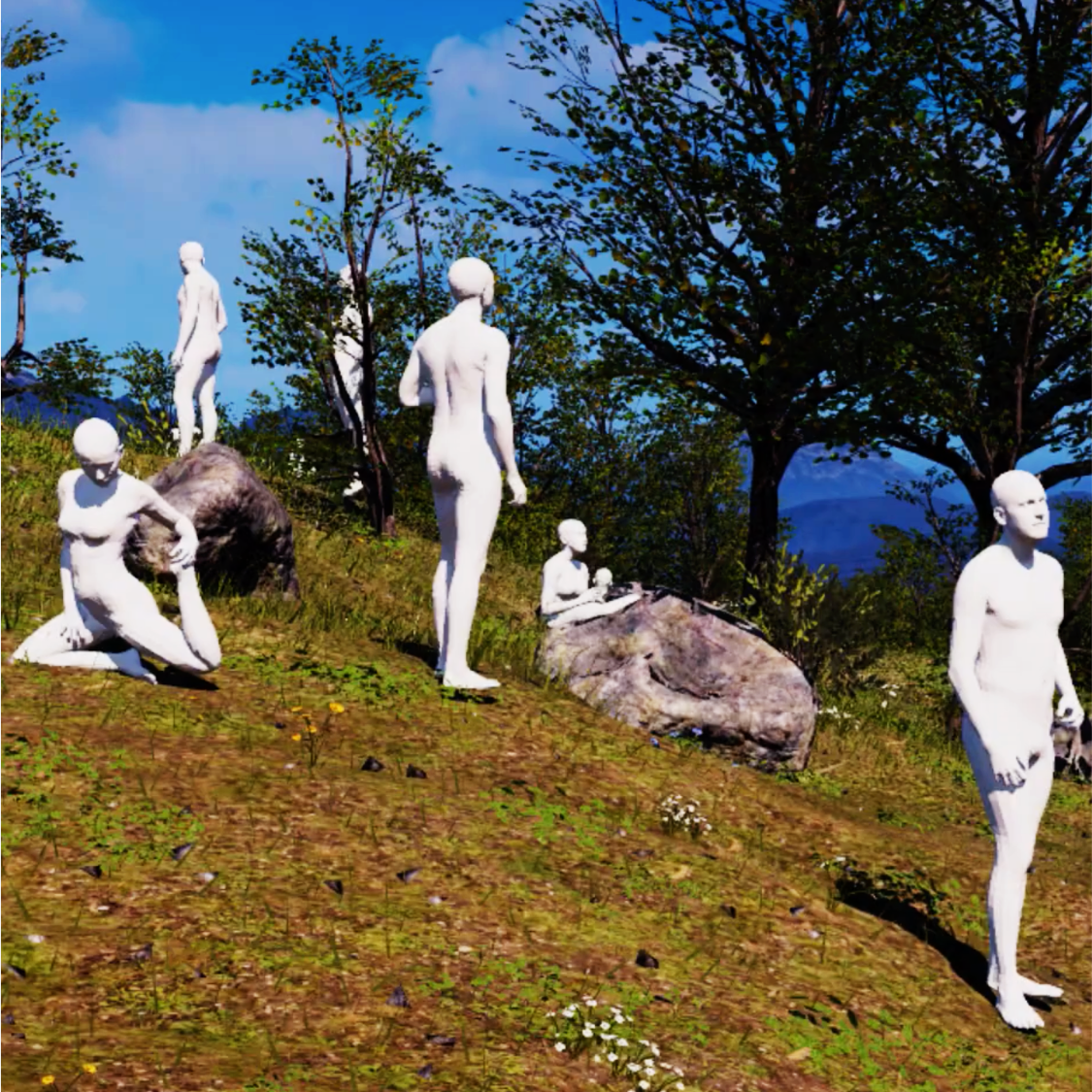

AGORA: Avatars in Geography Optimized for Regression Analysis
While the accuracy of 3D human pose estimation from images has steadily improved on benchmark datasets, the best methods still fail in many real-world scenarios. This suggests that there is a domain gap between current datasets and common scenes containing people. To obtain ground-truth 3D pose, current datasets limit the complexity of clothing, environmental conditions, number of subjects, and occlusion. Moreover, current datasets evaluate sparse 3D joint locations corresponding to the major joints of the body, ignoring the hand pose and the face shape. To evaluate the current state-of-the-art methods on more challenging images, and to drive the field to address new problems, we introduce AGORA, a synthetic dataset with high realism and highly accurate ground truth. Here we use 4240 commercially-available, high-quality, textured human scans in diverse poses and natural clothing; this includes 257 scans of children. We create reference 3D poses and body shapes by fitting the SMPL-X body model (with face and hands) to the 3D scans, taking into account clothing. We create around 14K training and 3K test images by rendering between 5 and 15 people per image us- ing either image-based lighting or rendered 3D environments, taking care to make the images physically plausible and photoreal. In total, AGORA consists of 173K individual person crops. We evaluate existing state-of-the- art methods for 3D human pose estimation on this dataset. and find that most methods perform poorly on images of children. Hence, we extend the SMPL-X model to better capture the shape of children. Additionally, we fine- tune methods on AGORA and show improved performance on both AGORA and 3DPW, confirming the realism of the dataset. We provide all the registered 3D reference training data, rendered images, and a web-based evaluation site at https://agora.is.tue.mpg.de/.

PoseNet3D: Learning Temporally Consistent 3D Human Pose via Knowledge Distillation
Recovering 3D human pose from 2D joints is a highly unconstrained problem. We propose a novel neural network architecture, PoseNet3D, that takes 2D joints as input and outputs 3D skeletons and SMPL pose parameters. By casting our learning approach in a Knowledge Distillation framework, we avoid using any 3D data such as paired 2D-3D data, unpaired 3D data, motion capture sequences or multi-view images during training. We first train a teacher network that outputs 3D skeletons, using only 2D poses for training. The teacher network distills its knowledge to a student network that predicts 3D pose in SMPL representation. Finally, both the teacher and the student networks are jointly fine tuned in an end-to-end manner using self-consistency and adversarial losses, improving the accuracy of the individual networks. Results on Human3.6M dataset for 3D human pose estimation demonstrate that our approach reduces the 3D joint prediction error by 18% or more compared to previous methods. Qualitative results show that the recovered 3D poses and meshes are natural, realistic, and flow smoothly over consecutive frames.

Learning to Generate Synthetic Data via Compositing
We present a task-aware approach to synthetic data generation. Our framework employs a trainable synthesizer network that is optimized to produce meaningful training samples by assessing the strengths and weaknesses of a `target' network. The synthesizer and target networks are trained in an adversarial manner wherein each network is updated with a goal to outdo the other. Additionally, we ensure the synthesizer generates realistic data by pairing it with a discriminator trained on real-world images. Further, to make the target classifier invariant to blending artefacts, we introduce these artefacts to background regions of the training images so the target does not over-fit to them. We demonstrate the efficacy of our approach by applying it to different target networks including a classification network on AffNIST, and two object detection networks (SSD, Faster-RCNN) on different datasets. On the AffNIST benchmark, our approach is able to surpass the baseline results with just half the training examples. On the VOC person detection benchmark, we show improvements of up to 2.7% as a result of our data augmentation. Similarly on the GMU detection benchmark, we report a performance boost of 3.5% in mAP over the baseline method, outperforming the previous state of the art approaches by up to 7.5% on specific categories.
C2F: Coarse-to-Fine Vision Control System for Automated Microassembly
In this paper, authors present the development of a completely automated system to perform 3D micromanipulation and microassembly tasks. The microassembly workstation consists of a 3 degree-of-freedom (DOF) MM3A® micromanipulator arm attached to a microgripper, two 2 DOF PI® linear micromotion stages, one optical microscope coupled with a CCD image sensor, and two CMOS cameras for coarse vision. The whole control strategy is subdivided into sequential vision based routines: manipulator detection and coarse alignment, autofocus and fine alignment of microgripper, target object detection, and performing the required assembly tasks. A section comparing various objective functions useful in the autofocusing regime is included. The control system is built entirely in the image frame, eliminating the need for system calibration, hence improving speed of operation. A micromanipulation experiment performing pick- and-place of a micromesh is illustrated. This demonstrates a three-fold reduction in setup and run time for fundamental micromanipulation tasks, as compared to manual operation. Accuracy, repeatability and reliability of the programmed system is analyzed.
Sub-cortical Shape Morphology and Voxel-based Features for Alzheimer's Disease Classification
Neurodegenerative pathologies, such as Alzheimer’s disease, are linked with morphological alterations and tissue variations in subcortical structures which can be assessed from medical imaging and biological data. In this work, we present an unsupervised framework for the classification of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) patients, stratifying patients into four diagnostic groups, namely: AD, early Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI), late MCI and normal controls by combining shape and voxel-based features from 12 sub-cortical areas. An automated anatomical labeling using an atlas-based segmentation approach is proposed to extract multiple regions of interest known to be linked with AD progression. We take advantage of gray-matter voxel-based intensity variations and structural alterations extracted with a spherical harmonics framework to learn the discriminative features between multiple diagnostic classes. The proposed method is validated on 600 patients from the ADNI database by training binary SVM classifiers of dimensionality reduced features, using both linear and RBF kernels. Results show near state-of-the-art approaches in classification accuracy (>88%), especially for the more challenging discrimination tasks: AD vs. LMCI (76.81%), NC vs. EMCI (75.46%) and EMCI vs. LMCI (70.95%). By combining multimodality features, this pipeline demonstrates the potential by exploiting complementary features to improve cognitive assessment.
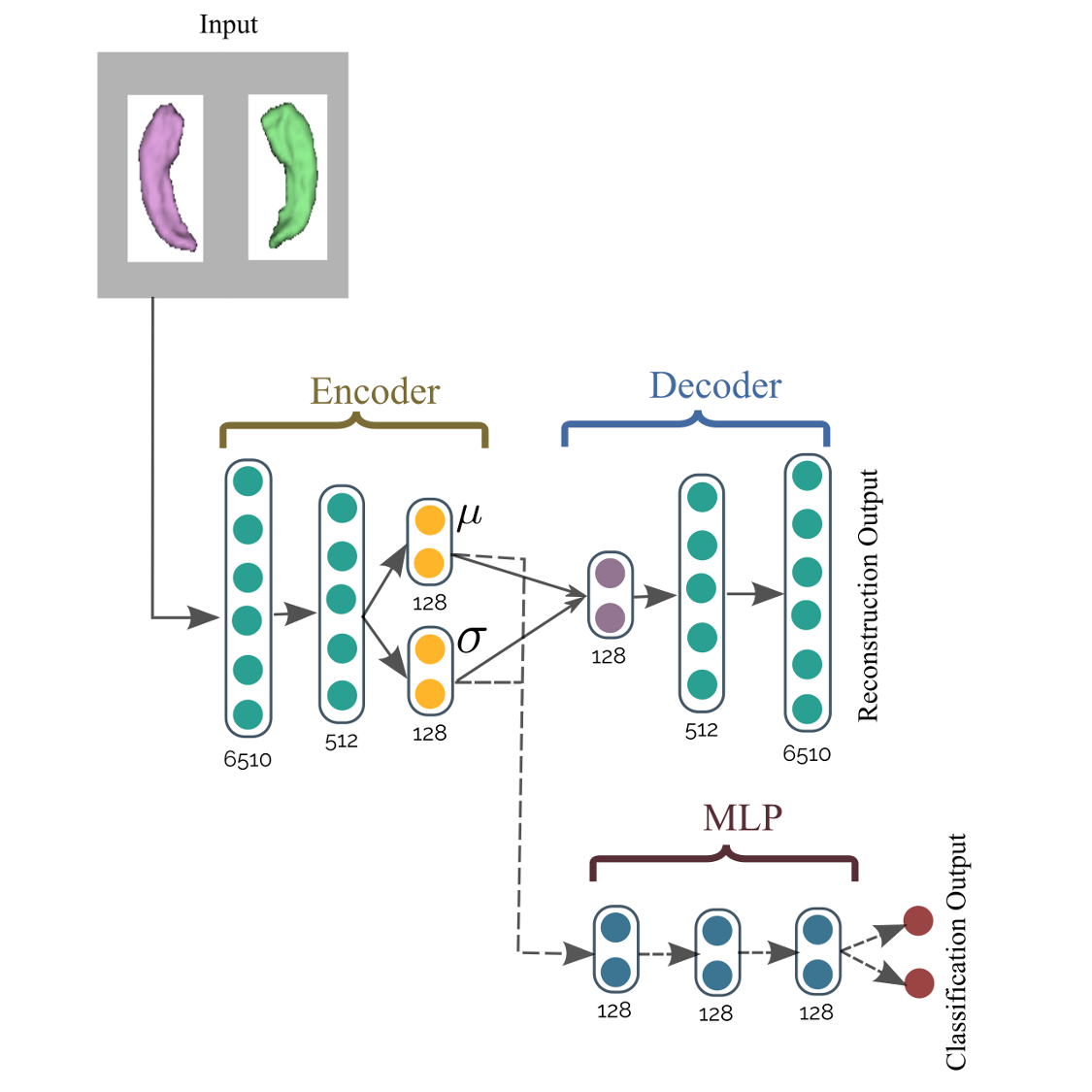
Deep Spectral-Based Shape Features for Alzheimer’s Disease Classification
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and mild cognitive impairment (MCI) are the most prevalent neurodegenerative brain diseases in elderly population. Recent studies on medical imaging and biological data have shown morphological alterations of subcortical structures in patients with these pathologies. In this work, we take advantage of these structural deformations for classification purposes. First, triangulated surface meshes are extracted from segmented hippocampus structures in MRI and point-to-point correspondences are established among population of surfaces using a spectral matching method. Then, a deep learning variational auto-encoder is applied on the vertex coordinates of the mesh models to learn the low dimensional feature representation. A multi-layer perceptrons using softmax activation is trained simultaneously to classify Alzheimer’s patients from normal subjects. Experiments on ADNI dataset demonstrate the potential of the proposed method in classification of normal individuals from early MCI (EMCI), late MCI (LMCI), and AD subjects with classification rates outperforming standard SVM based approach.
Patents
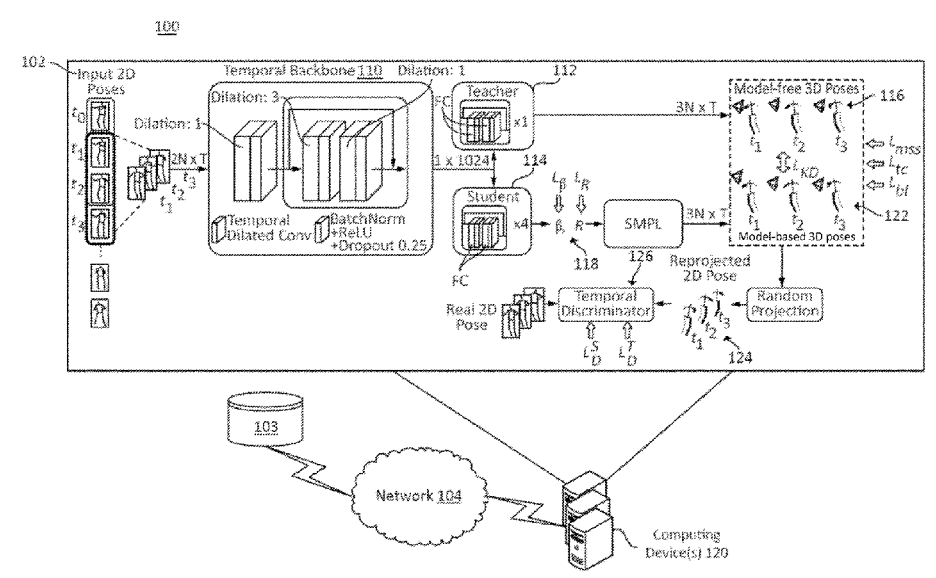
Three-dimentional Pose Estimation without 3D Data
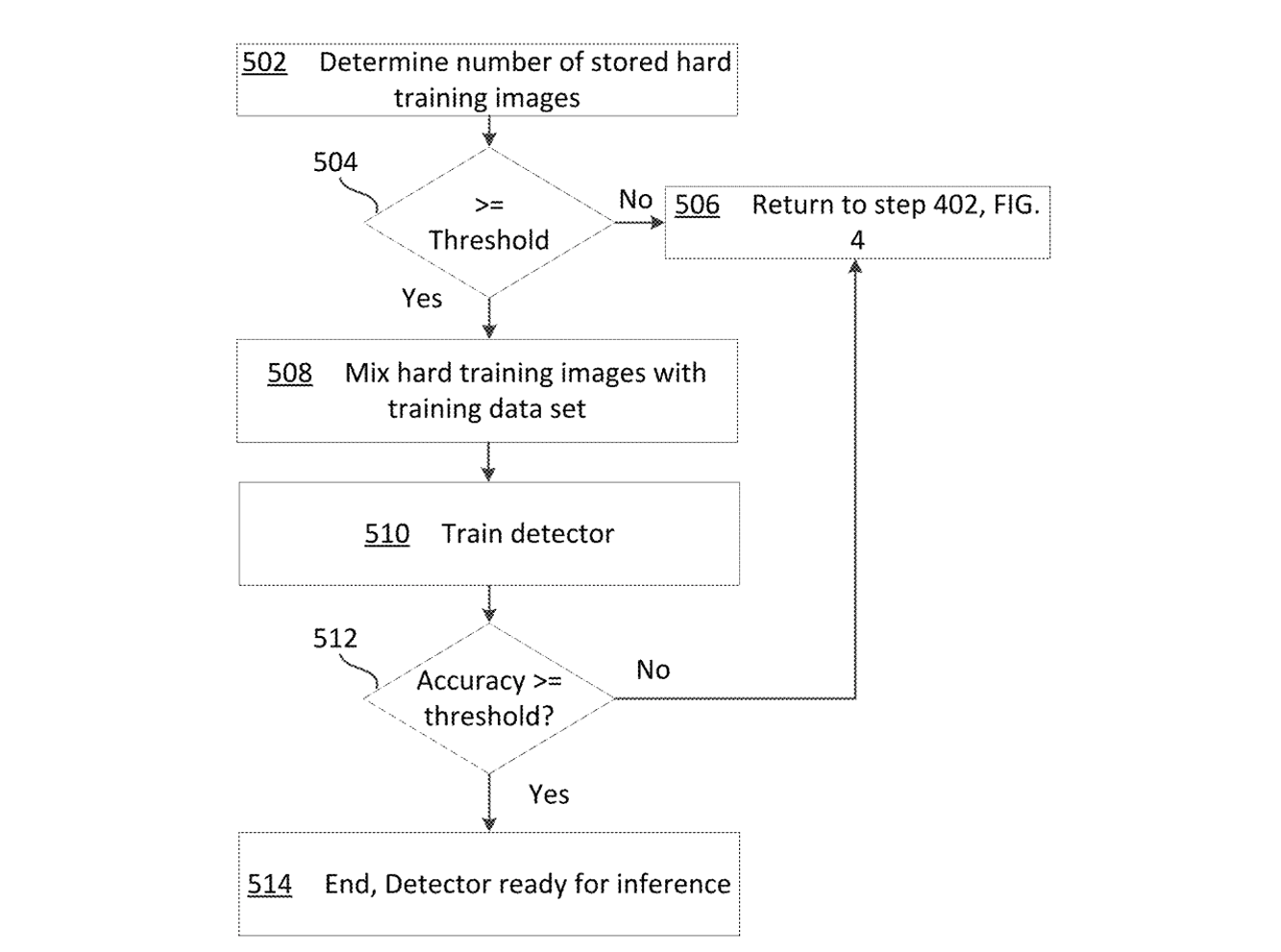
Generation of synthetic image data using three-dimensional models
Generation of synthetic image data for computer vision models
Miscellaneous
Some other unpublished work:

Learning Salient Objects in a Scene using Superpixel-augmented Convolutional Neural Networks
Moving object detection, tracking and classification from an unsteady camera